Tech
How to Make a Custom Music Streaming App 7 Steps for Creators

The music streaming market is predicted to expand by 5.14% (2023-2027), resulting in a market size of $18.56 billion by 2027. The industry is flourishing, and it’s no wonder. With the ease of listening to any track, anytime, anywhere, without downloading any files, music apps have been the preferred choice for music enthusiasts. But how do you build an app that streams music?
Although music streaming app development is not an easy task. With all the competition in this market, it requires lots of work and strategic thinking to create an app that is distinct from the rest and profitable.
Things to Consider Before Developing a Music Streaming App
Have an idea for your music streaming application? Perfect! It’s time to start work! Before you can create an app for streaming music, it is essential to consider several key elements.
Licensing
Music streaming requires complex licensing agreements with artists, record labels, and publishers. Music is intellectual property, and streaming without legal licensing is against the law. You’ll need permission from artists, record labels, and songwriters to legally stream music.
It’s also important to remember that music has become a language that can be used worldwide, and the reach of your app could extend beyond boundaries. Each country has regulations that must be followed, and adhering to them is crucial to avoid legal issues.
Get legal advice from experts in the field of music law and commit the time and funds to ensure your app functions within the confines of the law. This will create solid legal bases that support the growth of your music streaming venture and its long-term viability.
Music App Development Company
After you’ve gathered all the information you need, it is time to select the best company to execute your plans. This is among the most important steps to take when developing a music streaming application since the best company will walk you through the entire creation process, from the market overview through launch and even maintenance.
Choose a music streaming app development company with a history of producing efficient music applications. They should be able to comprehend the intricacies of the music world, such as licensing, metadata management, and the design of user experiences specific to streaming music.
Check out the company’s portfolio to see if they’ve worked on projects similar to yours. Get references from former clients to better understand the quality of their work and their trustworthiness.
The company should have an in-depth technical understanding of app development, including backend and frontend expertise. They should be experienced in creating apps for various platforms (iOS, Android, web) and familiar with streaming technology.
Market Overview
The world of music streaming is an ever-changing landscape in which understanding the dynamics of the market is crucial. A comprehensive market overview can help you create a competitive application. Industry giants such as Spotify, Apple Music, and Amazon Music have already established their own music libraries with large user bases. It is crucial to recognize these players to position your app correctly.
However, it’s important to identify the market you intend to target. The user base is the basis of the app’s success. Do you cater to popular audiophiles or lovers of music? Understanding the potential customers’ preferences can influence the features of your app and library of content.
This is why market overview is the primary goal of creating an app for streaming music.
Monetisation Strategy
Before you can create an app for streaming music, you must figure out how your app can generate income. It is important to consider your audience’s needs and long-term goals for your business. A balanced and user-focused method of monetization can generate revenue while also providing value for your music-loving fans.
There are a variety of various strategies for monetization:
- Subscription Models
- Ad-Supported Free Tier
- In-App Purchases
- Sponsored Content
- Data Monetisation
- Crowdfunding
It is essential to constantly modify and improve your method to achieve the ideal equilibrium between generating revenues, delivering the best value to your customers, and ensuring the longevity of your streaming music application.
How to Develop a Music Streaming App in 7 Steps?
If you’re a newbie in business or just a music fan, these actions will allow you to learn how to create your application. We’ll discuss designing your app, obtaining the appropriate permissions, selecting those who can help make your app appear professional, and then launching small to try the app.
Conduct Market Research
A thorough market study is the first element in establishing an effective music streaming application. Understanding your market in depth is essential to understand their preferences, demographics preferences, and issues.
Examine competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, features, and user feedback to learn more about what is working and what is not in the current marketplace. Analyzing users’ needs and preferences can help you identify the gaps your app could solve, thus creating a unique selling point (USP) that will set the app apart from other apps.
By leveraging this information, you can design an effective plan of action that is aligned with the market’s demands, ensuring that your app delivers an engaging and distinct experience that is a hit with potential customers.
Music Licensing
Obtaining the licenses needed to legally stream music is a crucial step in creating a music streaming application. This requires negotiating agreements with record labels and music publishers, rights organizations like ASCAP, BMI, and SESAC in the United States, and international counterparts such as PRS for Music in the UK and SOCAN in Canada.
They typically comprise mechanical licenses, public performance licenses, and synchronization licenses. These ensure you are legally granted the right to distribute and stream music to your platform. In addition, interacting with digital distribution and aggregators can make creating an extensive music catalog easier.
Given the ever-changing and complex nature of rights to music, staying current with the most recent regulations and developments in the field of music is vital to ensure compliance and avoid legal problems.
Tech Stack Selection
Choosing the right technology stack is crucial to building a robust and extensible music streaming application. Swift is the ideal programming language for developing apps for iOS because of its efficiency and compatibility with Apple’s platform.
In the case of Android, Kotlin is the preferred choice, with modern features for language and compatibility with Java. The backend infrastructure is crucial; cloud-based services like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Google Firebase provide scalable server solutions, solid data storage, and real-time database capabilities.
They also provide crucial features like authentication, analytics, and push notifications that are crucial for providing a smooth user experience. Furthermore, using the content delivery network (CDNs) will allow for effective media streaming, while using technologies such as GraphQL will increase the effectiveness of data queries.
If you select the correct technology stack, you will ensure that your application is reliable, efficient, and able to meet your users’ growing demands.
Develop the App
With a clearly defined plan and the right tech stack in place, the Next step is to begin coding and designing the application. Create a user-friendly interface that provides a simple navigation experience and a pleasant user experience.
Important features include building and managing playlists and allowing users to arrange their favorite songs. Advanced AI-driven suggestions can be utilized to give personalized music suggestions according to listener preferences and history, which improves user satisfaction and engagement.
You can ensure high-quality audio streaming using efficient encoders and adaptive bitrate streaming technology, which preserves the audio quality and optimizes the network’s performance under various conditions.
In addition, ensure that you have solid backend support that allows for immediate changes and seamless replay. This will ensure your app runs smoothly under various demands and delivers the same high-quality, consistent experience for every user.
Perform Integrations
Integrating third-party service providers is vital to improving the usability and experience of your streaming music application. Install secure and reliable payment processing options like Stripe, PayPal, or Apple Pay to handle subscriptions and purchases in-app.
Utilize analytics tools such as Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Firebase Analytics to track user behavior, app performance, engagement, and performance metrics. These tools can provide useful insights for continual improvement.
To authenticate users, use trusted services such as OAuth, Firebase Authentication, or Auth0 to ensure safe and efficient login procedures. In addition, it integrates seamlessly with social platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, which allow users to publish their favorite songs, playlists, or activities and utilize social logins for fast and effortless access to the application.
These integrations improve the app’s functionality and aid in a more cohesive and enjoyable user experience.
Testing and Refinement
A thorough testing and refinement process is vital to ensuring an app’s reliability and user satisfaction. This process involves rigorous testing to discover and fix bugs on a variety of platforms and operating systems to ensure compatibility and stability.
Testing performance is essential to determining the app’s speed of response, load times, and scalability in various circumstances, and security testing ensures that users’ data is secure from potential security risks and data breaches.
Testing the user’s satisfaction (UX) test is also crucial. It is focused on the app’s design, navigation system, and general usability to provide an enjoyable and intuitive experience. This includes automated testing to ensure even and consistent test coverage and manual testing to spot problems that automated tests could fail to detect.
When you focus on these areas with care to ensure an easy and smooth launch that delivers a flawless and reliable product for the users you serve, feedback from beta testers can offer invaluable insights into how users use the app and aid in fine-tuning the application.
Deploy the App
Preparing for the app’s launch requires several key steps to ensure a smooth launch and a positive initial reaction.
In the beginning, you must thoroughly study and follow the submission guidelines of the Google Play Store and Apple App Store and ensure that your application meets the technical, design, and content specifications. This includes creating appealing listings for the app store that include high-quality images, compelling descriptions, and appropriate keywords that will increase your app’s visibility.
Once your application is submitted, you should plan for feedback on the app and be prepared to make any necessary changes. Also, develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to advertise your app and draw users. This strategy should include a pre-launch excitement campaign on social media, along with influencer partnerships, email marketing, and content marketing.
Consider leveraging App Store optimization (ASO) methods such as paid advertising and PR efforts to boost awareness and increase downloads. Coordinating these activities will increase your app’s exposure, draw the attention of a large number of users, and ensure that your launch is successful.
The Key Takeaway
In the end, music streaming application development that is unique from the crowd requires the time and energy of a strategic plan. By incorporating key features such as an extensive music library and personalization, playlists, social sharing, and the ability to integrate, one can develop an online streamer service for music that offers an exceptional and rewarding user experience.
A smooth and user-friendly interface, easy navigation system, minimalist design, and speedy loading times are essential for success.
Tech
Guide to Unlocking More Power for Better Diesel Engine Performance

Diesel engines have long been valued for their durability, torque, and fuel efficiency, but many owners eventually wonder about unlocking additional performance from their vehicles. Whether you’re looking to improve towing capacity, enhance acceleration, or simply experience what your diesel engine can truly deliver, understanding your options is the first step.
The good news is that diesel engines are particularly responsive to performance modifications due to their robust construction and the way they generate power. This article explores the various approaches to increasing horsepower in diesel engines, from simple bolt-on upgrades to more comprehensive modifications that work together to transform your vehicle’s capabilities.
Cold Air Intake Systems
Replacing the factory air intake system with a cold air intake allows your engine to breathe more efficiently by drawing in cooler, denser air. Cooler air contains more oxygen molecules per volume, which supports more complete fuel combustion in the cylinders.
Most diesel engines are restricted by their stock intake systems, which prioritize noise reduction and cost over maximum airflow. Installing an aftermarket cold air intake typically involves removing restrictive airboxes and routing intake piping to draw air from outside the engine bay where temperatures are lower.
Performance Exhaust Systems
The exhaust system plays a crucial role in how efficiently your diesel engine expels combustion gases and makes room for fresh air intake. Stock exhaust systems often feature smaller diameter piping and multiple sound-dampening components that create backpressure.
Reducing this backpressure through larger diameter pipes and high-flow mufflers allows exhaust gases to exit more quickly. When exhaust gases leave the cylinders faster, the engine can complete its combustion cycle more efficiently and produce additional power.
Electronic Tuning and ECM Programming
Modern diesel engines are controlled by sophisticated computer systems that manage fuel delivery, injection timing, and boost pressure among other parameters. The factory programming in these engine control modules is typically conservative to accommodate various fuel qualities, climates, and driving conditions.
Performance tuning adjusts these parameters to optimize power output while maintaining reliability within safe operating ranges. Reprogramming can yield substantial horsepower gains because diesel engines respond particularly well to increased fuel delivery when paired with adequate air supply.
Diesel Turbo Chargers
Turbo charger installation or upgrading represents one of the most effective methods for increasing diesel engine horsepower significantly. Moreover, diesel turbo chargers utilise gases from the exhaust to spin a turbine that, through the compression of incoming air, will force more oxygen into the combustion chambers than natural aspiration allows.
Many diesel engines come with factory turbochargers that can be replaced with larger or more efficient units designed for higher boost pressures. Professional installation services are available through diesel performance shops, specialized truck service centers, and some general automotive performance facilities that have technicians trained in forced induction systems.
Fuel System Upgrades
The fuel delivery system must keep pace with increased air supply when pursuing higher horsepower levels in diesel engines. Upgrading fuel injectors to units with higher flow rates ensures adequate fuel reaches the cylinders when you’ve added other performance modifications.
High-performance fuel pumps may also be necessary to maintain proper fuel pressure throughout the RPM range. These components work together to support complete combustion when your engine is moving significantly more air than stock configuration.
Intercooler Enhancement
When air is compressed by a turbocharger, it heats up substantially, which reduces its density and oxygen content. An intercooler cools this compressed air before it enters the engine, restoring density and providing more oxygen for combustion.
Upgrading to a larger or more efficient intercooler than the factory unit allows for lower intake air temperatures even under sustained high-boost conditions. Cooler intake temperatures also reduce the risk of engine knock and allow for more aggressive tuning parameters.
Injection Timing Adjustments
The precise moment when fuel is injected into the combustion chamber significantly affects how efficiently that fuel burns and how much power it produces. Advancing injection timing causes fuel to ignite earlier in the compression stroke, which can increase cylinder pressure and power output.
However, timing adjustments must be carefully calibrated because excessive advancement can cause rough running, increased engine noise, and higher combustion temperatures. Electronic control systems on modern diesels allow for precise timing adjustments through programming rather than mechanical modifications.
Supporting Modifications for Reliability
Increasing horsepower places additional stress on various engine components that may need reinforcement to maintain long-term reliability. Upgraded head studs or bolts help secure the cylinder head against higher combustion pressures from performance modifications.
Transmission upgrades often become necessary because factory transmissions may not be rated for the increased torque that diesel performance modifications produce. Enhanced cooling systems including larger radiators and auxiliary transmission coolers help manage the additional heat generated by higher power output.
Maintenance Considerations with Performance Upgrades
Engines producing significantly more power than stock require more attentive maintenance schedules to ensure longevity and continued performance. Oil changes may need to occur more frequently because higher boost pressures and combustion temperatures place greater demands on engine oil.
Monitoring boost levels, exhaust gas temperatures, and other vital parameters through aftermarket gauges helps you understand how modifications affect engine operation. Regular inspections of turbocharger components, intercooler connections, and fuel system elements catch potential issues before they result in failures or performance degradation.
Boost diesel engine horsepower by improving airflow (intake/exhaust), optimizing fuel delivery, and adding forced induction. Successful enhancement requires complementary modifications aligned with specific goals (towing, acceleration, responsiveness). Research, professional consultation, and proper maintenance ensure increased power while preserving reliability.
Tech
Techenhance: Empowering Digital Transformation Through Innovation and Technology Excellence

In a rapidly evolving digital world, businesses are under constant pressure to innovate, optimise, and future-proof their operations. Whether it’s adopting emerging technologies, strengthening IT infrastructure, or building customer-centric digital experiences, companies need more than just tools – they need a technology partner capable of driving sustainable success. This is where Techenhance emerges as a trusted and forward-thinking powerhouse in the global tech landscape.
As organisations accelerate their digital transformation journeys, Techenhance provides the expertise, frameworks, and strategic guidance required to navigate this complex terrain. Their ability to combine cutting-edge technology with a consultative approach makes them a preferred choice for businesses across industries.
What Makes Techenhance a Standout Digital Partner?
At its core, Techenhance is designed to elevate businesses by enhancing their technological capabilities. Rather than simply delivering solutions, they architect scalable digital ecosystems that evolve as the business grows. Their approach focuses on agility, efficiency, and long-term value — three essentials for modern enterprises.
With a robust portfolio of services and a team of seasoned technology consultants, Techenhance offers end-to-end digital transformation support that covers everything from ideation to execution and ongoing optimisation.
1. Comprehensive Digital Transformation Services
Digital transformation is more than adopting new technology — it’s about reshaping business processes, elevating experiences, and unlocking new opportunities. Techenhance helps companies redesign their operations using modern digital strategies that align with market shifts and customer expectations.
Their transformation services span across:
- Business process optimisation
- Enterprise automation
- Cloud and infrastructure modernisation
- Technology roadmap creation
- Data-driven decision frameworks
- Application modernisation and migration
This holistic approach ensures that every aspect of a business’s digital ecosystem works together to drive growth.
2. Expertise Across Modern Technologies
One of the biggest strengths of Techenhance lies in its technically diverse team. The company keeps pace with evolving technology trends, ensuring clients are never left behind. They deliver solutions across a wide spectrum of modern technologies including:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- Cloud computing
- DevOps and automation
- Data science and analytics
- IoT (Internet of Things)
- Full-stack application development
- Cybersecurity and compliance solutions
This broad expertise empowers businesses to adopt the right tools for their specific challenges, enabling smarter operations and improved scalability.
3. Custom Software and Product Development
In today’s competitive environment, cookie-cutter solutions are no longer enough. Businesses require highly tailored digital products that address unique operational needs and customer journeys.
Techenhance specialises in developing customised software solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing business workflows. Their product development lifecycle emphasises innovation, usability, and performance. From concept creation to product deployment and maintenance, every stage is handled with meticulous attention to quality and user experience.
4. A Customer-Centric Approach
Technology alone is not enough — understanding the client’s business landscape is equally vital. Techenhance excels in combining technical knowledge with a deep understanding of industry-specific needs.
They follow a consultative model that includes:
- Detailed need analysis
- Business use-case mapping
- ROI-driven planning
- Transparent communication
- Continuous improvement cycles
This ensures that solutions are not only technically strong but also aligned with strategic business goals.
Whether it’s a startup aiming to build its first product or an enterprise seeking to modernise legacy systems, Techenhance adapts its approach to deliver maximum value.
5. Delivering End-to-End IT Management
Many organisations struggle with maintaining secure, scalable, and efficient IT operations. Techenhance offers complete IT management and support services that ensure seamless day-to-day functioning.
Their IT services include:
- Infrastructure monitoring
- Network management
- Security and compliance
- Cloud optimisation
- Disaster recovery setup
- 24/7 IT support services
This allows businesses to focus on core objectives while relying on Techenhance to maintain operational stability.
6. Industry-Focused Technology Solutions
Digital transformation isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different industries have unique challenges, regulatory requirements, and technological needs. Techenhance’s industry-specific expertise helps companies implement customised digital solutions that fit their sector.
They work across sectors such as:
- Financial services
- Healthcare
- Retail and eCommerce
- Logistics and transportation
- Real estate
- Manufacturing
- Education and e-learning
By aligning technology with industry demands, Techenhance ensures faster adoption, reduced risk, and greater long-term impact.
7. Building Scalable Digital Experiences
Modern customers value seamless, intuitive digital interactions. Techenhance helps businesses create customer-centric experiences across mobile apps, websites, and digital platforms.
Their experience design services include:
- UX/UI design
- Customer journey optimisation
- Prototyping and testing
- Performance and usability enhancement
With user experience becoming a key differentiator, Techenhance’s strategic design capabilities help businesses stand out in a crowded marketplace.
8. Strong Focus on Innovation and Future-Readiness
The digital world changes fast — and businesses must innovate to stay relevant. Techenhance invests heavily in emerging technologies and research to ensure clients are always one step ahead.
They help organisations integrate:
- Predictive analytics
- Automation tools
- Machine learning algorithms
- Cloud-native architectures
- Modern development lifecycles
- Real-time monitoring dashboards
By future-proofing operations, Techenhance enables businesses to pivot quickly as market demands shift.
9. Why Businesses Trust Techenhance
Companies partnering with Techenhance benefit from:
Proven technical expertise
Their experienced team delivers reliable, high-performance digital solutions.
Tailored strategies
Solutions are designed based on business goals, not generic templates.
Transparent processes
Clients enjoy full visibility at every project stage.
Commitment to long-term value
Support extends beyond deployment, ensuring ongoing optimisation.
Competitive advantage
By leveraging advanced technologies, businesses gain an edge in their industry.
From startups to established enterprises, Techenhance empowers organisations to unlock new digital opportunities and scale confidently.
Final Thoughts
Digital transformation is no longer optional — it’s a strategic necessity. As technology becomes the backbone of modern business, companies must adopt innovative, scalable solutions to stay competitive. Techenhance stands out as a reliable partner that brings together expertise, innovation, and customer-centricity to deliver exceptional digital outcomes.
Whether you’re aiming to build a new product, modernise existing technology, strengthen your IT infrastructure, or adopt advanced digital tools, Techenhance provides the end-to-end support needed to succeed.
For businesses planning their next phase of digital evolution, partnering with a trusted technology expert like Techenhance can make all the difference.
Tech
Top Benefits of Investing in a Robotic Welding Machine
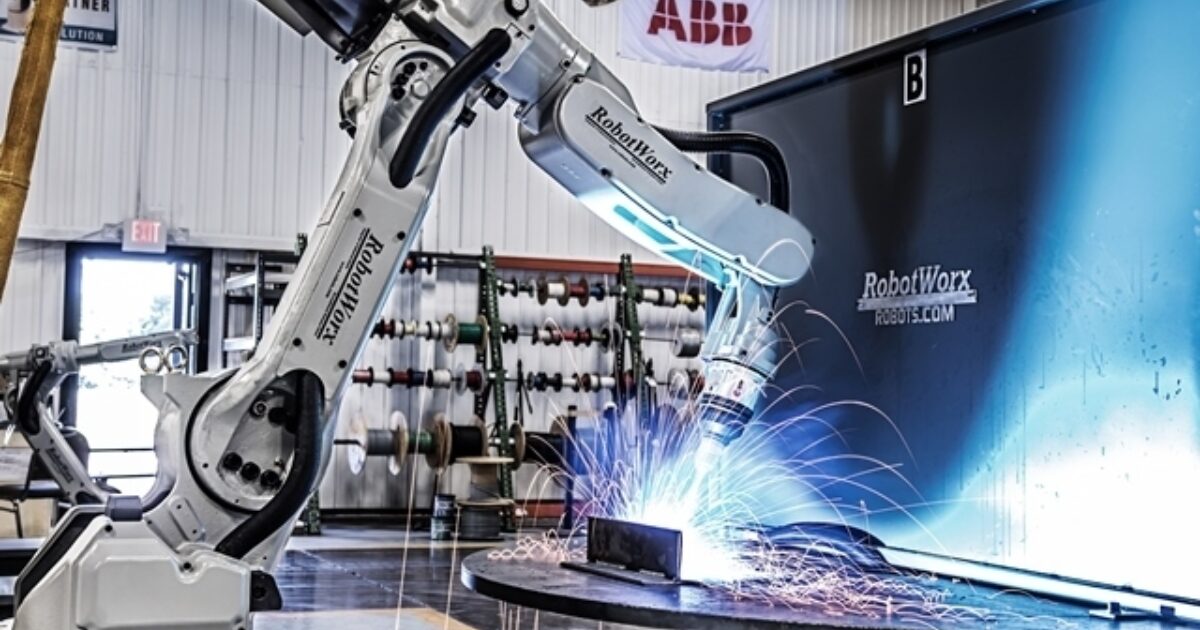

In today’s competitive manufacturing world, automation is essential, not optional. One of the most significant advancements is the use of robotic welding machines on production lines. These systems are transforming industries by improving efficiency, consistency, and safety in welding operations.
Welding is critical for creating strong, reliable products, but it has traditionally been labor-intensive and hazardous. Robotic welding machines automate the process, providing precise, consistent welds, increasing production speed, reducing errors, enhancing safety, and minimizing material waste.
This guide explores how robotic welding machines are revolutionizing production, highlighting their benefits, applications, and key considerations for implementation. Whether upgrading existing operations or introducing automation, understanding robotic welding is essential to stay competitive in modern manufacturing.
What is a Robotic Welding Machine?
A robotic welding machine is an automated system that uses programmable robotic arms to perform welding with high precision and efficiency. Unlike human welders, robots can work longer hours, deliver consistent welds, and reduce material waste.
These systems often use robotic arms like PUMA-type or UR-type, designed to maximize performance while making the most of available space and avoiding collisions.
Some advanced robots can even mimic the techniques of skilled welders through operator skill modeling, allowing them to handle complex welds that once required expert human hands. In short, robotic welding blends human expertise with robotic precision, improving productivity, weld quality, and overall manufacturing performance.
How Does Robotic Welding Work?
Robotic welding works by using automated systems to perform welding tasks with high precision and efficiency. These systems rely on several key components that work together to ensure consistent, high-quality welds:
Components and Functionality
- Robotic Manipulator: A six-axis articulated arm that moves the welding torch along precise paths.
- Welding Torch: Mounted on the arm, it delivers the welding arc and filler material.
- Power Supply: Controls electrical parameters to maintain a stable arc and high-quality weld.
- Wire Feeder: Regulates the flow of filler material for uniform welds.
- Sensors and Cameras: Monitor the weld in real time, allowing automatic adjustments to maintain quality.
- Central Controller: Coordinates all components and executes programmed commands for seamless operation.
Achieving Efficiency and Precision
Robotic welders can operate continuously without fatigue, increasing productivity compared to human welders. They use programmed control of travel speed, arc length, and heat input to create welds with precise tolerances. Real-time sensors enable seam tracking and dynamic adjustments for consistent weld quality. Robots can reach challenging positions and maintain optimal torch angles, preventing defects like porosity or incomplete fusion.
Robotic welding combines automated control, advanced sensors, and precise mechanical movement to deliver efficient, accurate, and reliable welding results.
Top Benefits of Investing in a Robotic Welding Machine
Investing in a robotic welding machine can greatly improve manufacturing processes. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Enhanced Productivity
Robotic welders can work continuously without breaks, completing tasks faster than human welders and increasing overall production speed.
2. Consistent and High-Quality Welds
Robots produce uniform welds, reducing defects, errors, and material waste, which ensures a higher-quality end product.
3. Reduced Labor Costs
Automation reduces the need for skilled welders, allowing companies to use their staff for other important tasks and improve overall efficiency.
4. Improved Safety
Robots handle hazardous tasks, such as exposure to intense heat and fumes, reducing the risk of workplace injuries.
5. Lower Material Waste
Robotic systems can be programmed for precise material usage, saving resources, cutting costs, and supporting sustainability.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
Robotic welders are flexible and adaptable, letting manufacturers handle various welding tasks and adjust production quickly to meet changing demands.
Considerations Before Investing
- High Initial Investment: Robotic welding systems can be expensive upfront, but long-term savings and efficiency gains often make the investment worthwhile.
- Technical Expertise Required: Operating and maintaining robotic systems requires training and specialized knowledge, so investing in staff education is crucial.
Robotic welding machines offer increased productivity, consistent quality, lower labor costs, improved safety, and reduced material waste. While they require an initial investment and technical expertise, their long-term benefits make them a smart choice for modern manufacturing operations.
Applications Across Industries
Robotic welding machines are transforming manufacturing by automating complex and repetitive tasks with precision and efficiency. Here’s how they are used in key sectors:
- Automotive Manufacturing
Robotic welding is essential in car production, automating the assembly of car bodies, frames, and components. Robots perform spot welding, seam welding, and other processes quickly and accurately, ensuring consistent quality while reducing labor costs. This helps produce lightweight, high-strength vehicles.
- Aerospace and Heavy Machinery
In aerospace, robotic welding provides the precision needed for manufacturing aircraft components like wings, fuselages, and landing gear. It is also used in heavy machinery production, including construction equipment, where strong and durable welds are critical.
- Electronics, Construction, and Other Industries
Robotic welding is applied in electronics for assembling metal parts such as computer chassis and smartphone frames. In construction, robots fabricate steel structures, bridges, and buildings, ensuring structural integrity. The technology is also used in shipbuilding, energy infrastructure, and consumer goods manufacturing, showing its versatility.
Robotic welding machines boost productivity, maintain high-quality welds, and improve safety across a wide range of industries, making them a valuable investment for modern manufacturing.
Future Outlook of Robotic Welding Machines
The future of robotic welding is being shaped by advanced technologies, making it more adaptable, accessible, and useful across industries.
- AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning allow robotic welding systems to learn from real-time data, optimize welding settings, and detect defects during operations. This makes robots more adaptable, enabling them to handle different materials and conditions with improved precision and efficiency.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots) for SMEs
Cobots are designed to work safely alongside humans without safety cages. They are affordable, easy to program, and flexible, making them ideal for small and medium-sized businesses. Cobots handle repetitive or precision welding tasks, freeing skilled welders to focus on more complex work.
- Expanding Applications Across Industries
Robotic welding is no longer limited to automotive or aerospace. Its use is growing in electronics, construction, renewable energy, and more. For example, in the automotive sector, robots perform spot and seam welding on car panels, frames, and exhaust systems, ensuring fast, precise, and consistent welds.
AI and machine learning are making robotic welding systems smarter and more adaptable, while collaborative robots are making automation accessible to smaller companies. With applications spreading across diverse industries, robotic welding is becoming a versatile and essential tool in modern manufacturing.
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoThe Role Of Veterinary Hospitals In Preventing Zoonotic Diseases
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoWhy Preventive Dentistry Provides Lasting Value For Families
-
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoSafe and Effective IV Therapy The Woodlands Explained
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoFawkes Market – The Leading UK Darkweb Market
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days ago3 Cosmetic Dentistry Options That Support Confidence At Any Age
-
 News7 days ago
News7 days ago4 Restorative Dentistry Options To Replace Missing Teeth
-

 Education6 days ago
Education6 days ago10 Certifications With Real-World Value and Fast Financial Returns
-
 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoWhy Digital Technology Is Transforming The Dental Patient Experience


